ClodronateLiposomes.org |
||||
Welcome
|
||||
Liposomes as a tool to manipulate macrophage functionFrom an evolutionary point of view, macrophages are ancient cells. They form the core of the natural immune system and did appear long before the cells forming together the complex immune system of the higher vertebrates. As a consequence, during the evolution, they did acquire functions both in natural immune reactions and in the regulation of functions of many non-phagocytic cells. The latter functions are mainly mediated by soluble molecules such as cytokines and chemokines. Macrophages are also involved in 'homoiostasis' of the body by ingesting and digesting microorganisms or non-self particles and macromolecules. Digestion is in turn mediated by their lysosomal enzymes. Liposomes are artificially prepared lipid vesicles, consisting of concentric phospholipid bilayers entrapping aqueous compartments. They can be used to encapsulate strongly hydropihilic molecules solved in aqueous solutions, such as clodronate, a non-toxic bisphosphonate, developed for human application. Freely solved clodronate will not cross liposomal or cellular phospholipid membranes. After injection, liposomes, used as Trojan horses in this case, will be ingested and digested by macrophages followed by intracellular release and accumulation of clodronate. At a certain intracellular concentration, clodronate induces apoptosis of the macrophage. By this approach, i.e. by creating an animal with macrophage depleted tissues or organs, functional aspects of macrophages are studied 'in vivo' in many collaborative projects. Moreover, promising results were obtained by application of clodronate liposomes for suppression of macrophage activity in various models of autoimmune diseases, transplantation, neurological disorders and gene therapy. 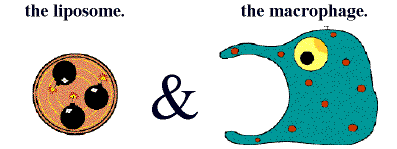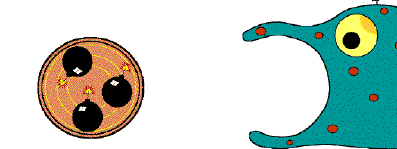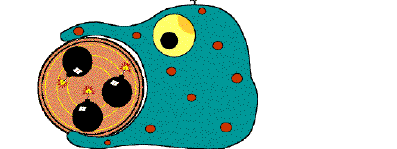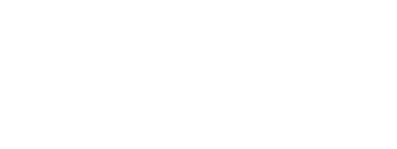 |
||||
Copyright (C) 2006 Dr. Nico van Rooijen - All rights reserved. |
||||
